

△ Huachuang Hongdu Highly Reliable Solid Lasers
With the rapid development of laser technology,solid-state lasers with their high power,high efficiency, long life and other advantages have played an important role in industrial processing,medical and cosmetic,military and national defense.However,with the increasing complexity and stringency of application scenarios,the reliability requirements of lasers are becoming more and more stringent.As the ” heart ” of the laser,the reliability of the optical system directly determines the overall performance and life of the laser.
This article is the first of the optical reliability series in the “high reliability” column.Due to its detailed content,it will be published in two parts.This is the first part,we will focus on optical design,selection of optical components and optimization of solid-state laser manufacturing process,to reveal how to build a solid foundation of laser optical reliability from the source of design and manufacturing.
Optical scheme design and optical component selection are the first steps to ensure the optical reliability of lasers.
① Analog optical path transmission
For example,in resonance cavity design,by adjusting the mirror curvature and cavity length and optimizing the pattern matching parameters,the probability of higher-order mold production can be significantly reduced,thereby improving the stability and monomode nature of laser output.
② Predicting the effect of thermal lensing
For example,for high-power solid lasers,thermal deformation can be effectively suppressed by optimizing the cooling system layout to ensure that spot sizes remain stable over long periods of operation.
③ Simulate different work conditions
For example,in portable lasers,the lightweight and highly rigid bracket design reduces the interference of external vibrations on spot positioning and improves the reliability of the laser in dynamic environments.
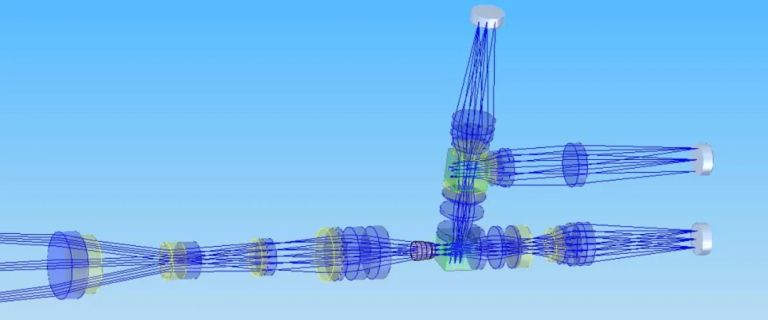
△ Optical Simulation Examples
Ultimately,through the combination of multiphysics field simulation and experimental verification,the optical solution can be optimized to ensure that lasers can maintain high performance output in complex application scenarios.
① Pick quality materials
For example,when selecting a laser crystal,it should be ensured that it has high purity and a uniform dispersion distribution to reduce the effect of thermal lensing effects and thermal stress on laser performance.
② Consider the conditions of use
For example,for high-power lasers, optical components with high reflectivity/high transmission rates on the surface should be chosen to reduce the loss of light energy and improve the utilization of light energy.A multilayer membrane system design is used to increase the threshold value of the optical components against laser damage and extend their service life.

△Laser Crystals and Highly Damaging Laser Lenses
Optimization of the solid laser manufacturing process is a key part of improving the optical reliability of lasers,including the processing of optical components,semi-finished product production, laser debugging process and cleanliness control.
Ensure the quality and precision of the machining
For example,advanced polishing techniques and equipment should be used in the polishing process of optical components to ensure that the surface roughness of outstanding components reaches nanoscale to improve their optical performance and service life.
① Control of mechanical stress
For example,in the assembly of laser lenses and heat frame components,a low stress adhesive process is required.Furthermore,finite element analysis simulations and tests validate the stress distribution under the heat cycle,optimize the thickness of the bonding layer to match the thermal expansion coefficient of the material,thereby reducing the interface shear stress caused by temperature change.At the same time, the structural stability of the semi-finished product is verified through environmental adaptation testing to ensure that there is no stress accumulation caused by performance degradation in long-term use.
② Upgrade the welding process
For example, in the welding of laser crystals and copper heat sink, flakes can be used to fill the welding process, effectively improving the thermal conductivity and reducing the residual stress of the welding.
For high-power laser crystals, for example, a microchannel cooling structure can be designed whereby the cooling tube is integrated with the crystal base through a welding process, making the cooling liquid directly contact the back of the crystal. At the same time, the temperature distribution of the welding interface is simulated through finite element thermal analysis, optimizing the thickness of the solder layer and avoiding the concentration of thermal stress due to thermal expansion mismatch.
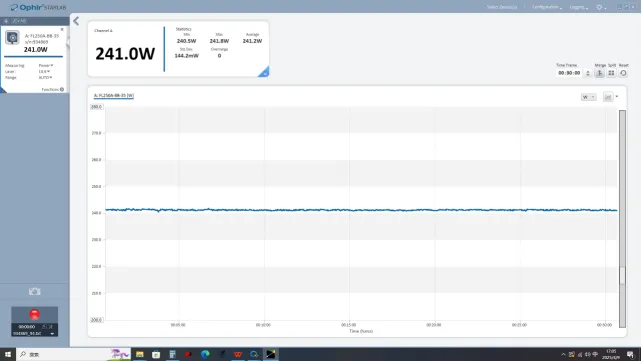
△ Output Stability of High-power Lasers Based on Huachuang Hongdu’s High Reliability Semi-finished Products
Experiments show that the laser crystal with precision welding technology can improve its heat dissipation performance by 40%,The output power stability is improved to ± 0.2%,It provides a key guarantee for the long-term reliable operation of high-power lasers.
① Reduce component position errors
For example,high-precision assembly jigs and adjustment structures ensure that relative positional errors between optical components are controlled within microns,thereby improving laser beam quality and stability.
② Reduction of mechanical stress on components

△ Huachuang Hongdu Highly Reliable Solid Laser Tuning
In the manufacturing process of solid-state lasers,one of the key links is to strictly control the cleanliness of optical components,semi-finished components and laser cavity.Throughout the assembly and commissioning phase,it is essential to ensure that the laser and all its components are kept in a constant temperature and humidity,dust-free environment.Specific measures include:
① Dustless Storage Process
② Clean assembly debugging
For example,in the process of laser crystal assembly and bonding of lenses,A second cleansing table needs to be used in the cleanroom to isolate the operating area,prevent the particles brought by people or equipment from contaminating the bonding interface,and monitor the environmental parameters in real time through a temperature and humidity sensor to ensure that the bonding process is not disturbed by the environment.In the laser debugging process, the risk of human pollution is reduced through the operation of anti-static workstations and dustless gloves specifically designed for the cleanroom.

△ Huachuang Hongdu Highly Reliable Solid Laser 1000-Grade Production Workshop
The high reliability of solid lasers is no accident.It derives from precision optical design and simulation, and becomes a rigorous manufacturing process that covers many dimensions of machining, assembly,clean control and more. From the two cornerstones of the design and process discussed above, we are able to shape lasers’ outstanding optical stability and long life from the source.
In the next section,we will continue to explore how high-reliability lasers can maintain stable and reliable operation in a variety of harsh application scenarios by improving environmental adaptability and building intelligent maintenance monitoring strategies.Stay tuned.
Trailer for the series
This paper opens the “High Reliability” series of in-depth analyses of optical reliability.In the next section, we will focus on environmental adaptation improvement and maintenance monitoring strategies.Stay tuned!

